- The row-columnar engine in makes queries up to 350x faster, ingests 44% faster, and reduces storage by 90%.
 This page shows you how to rapidly implement the features in that enable you to
ingest and query data faster while keeping the costs low.
This page shows you how to rapidly implement the features in that enable you to
ingest and query data faster while keeping the costs low.
Prerequisites
To follow the steps on this page:- Create a target with time-series and analytics enabled. You need your connection details. This procedure also works for .
Optimize time-series data in s with
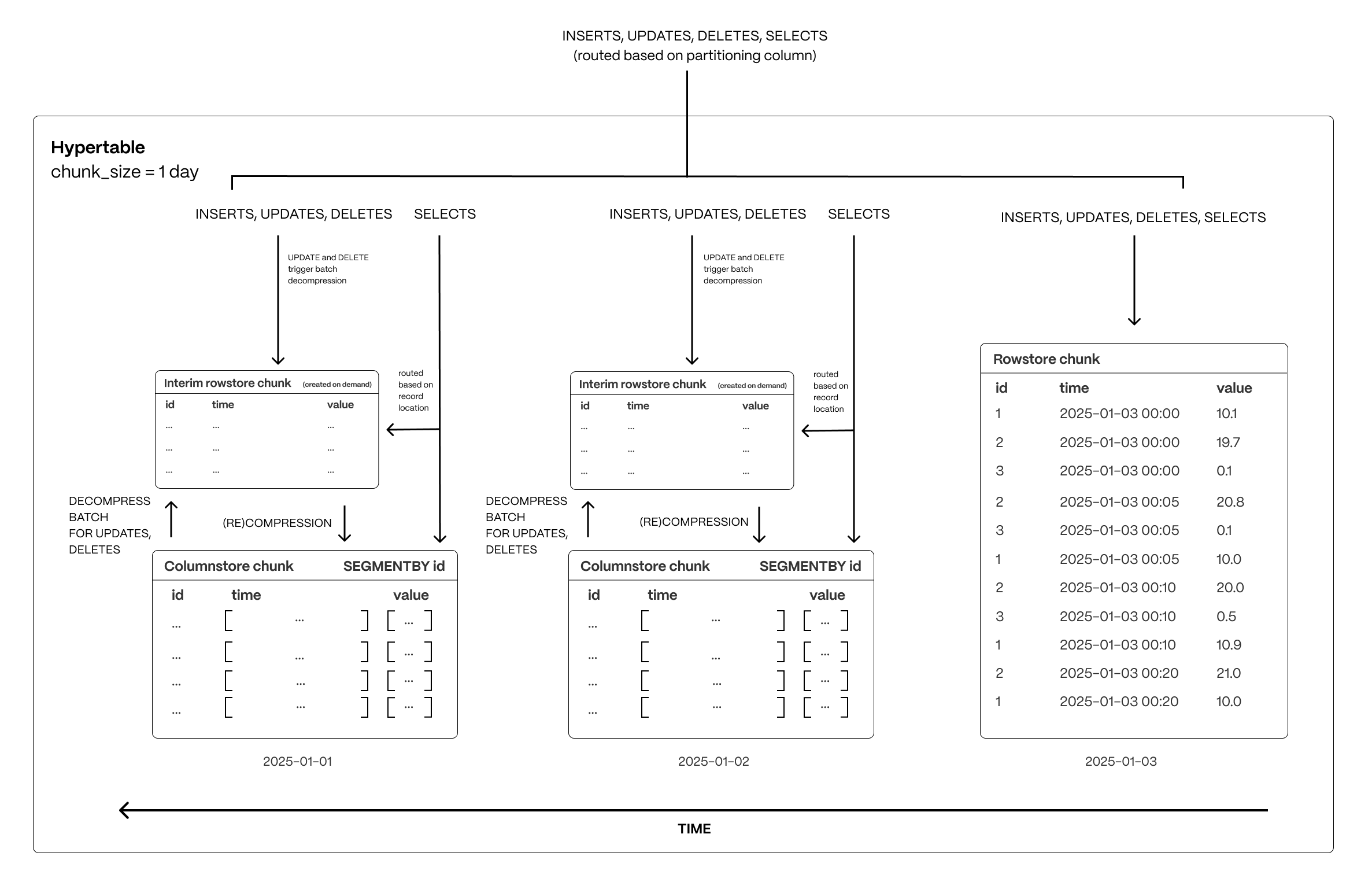
Time-series data represents the way a system, process, or behavior changes over time. _CAPs are tables that help you improve insert and query performance by automatically partitioning your data by time. Each is made up of child tables called s. Each is assigned a range of time, and only contains data from that range. When you run a query, identifies the correct and runs the query on it, instead of going through the entire table. You can also tune s to increase performance even more.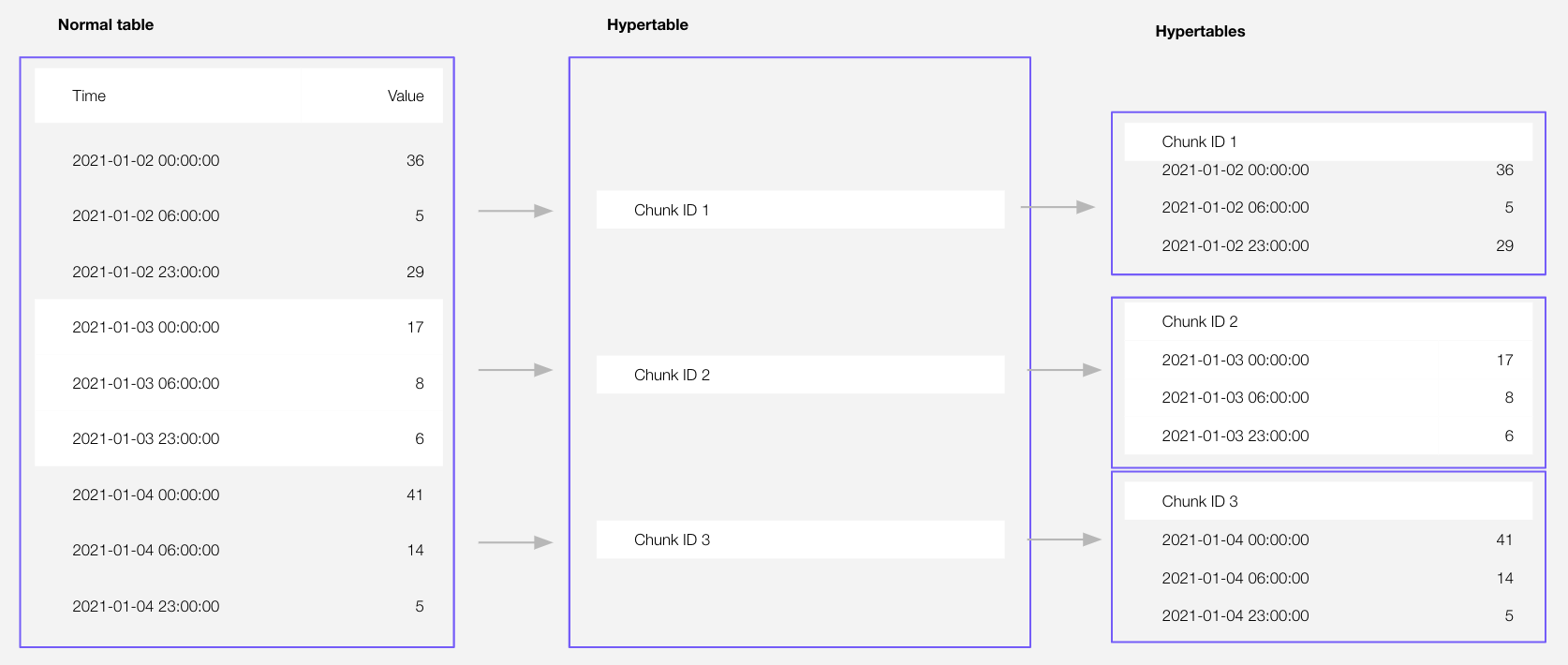 is the hybrid row-columnar storage engine in used by . Traditional
databases force a trade-off between fast inserts (row-based storage) and efficient analytics
(columnar storage). eliminates this trade-off, allowing real-time analytics without sacrificing
transactional capabilities.
dynamically stores data in the most efficient format for its lifecycle:
is the hybrid row-columnar storage engine in used by . Traditional
databases force a trade-off between fast inserts (row-based storage) and efficient analytics
(columnar storage). eliminates this trade-off, allowing real-time analytics without sacrificing
transactional capabilities.
dynamically stores data in the most efficient format for its lifecycle:
- Row-based storage for recent data: the most recent chunk (and possibly more) is always stored in the , ensuring fast inserts, updates, and low-latency single record queries. Additionally, row-based storage is used as a writethrough for inserts and updates to columnar storage.
- Columnar storage for analytical performance: chunks are automatically compressed into the , optimizing storage efficiency and accelerating analytical queries.
-
Import some time-series data into s
-
Unzip crypto_sample.zip to a
<local folder>. This test dataset contains:- Second-by-second data for the most-traded crypto-assets. This time-series data is best suited for optimization in a hypertable.
- A list of asset symbols and company names. This is best suited for a regular relational table.
-
Upload data into a :
To more fully understand how to create a , how s work, and how to optimize them for
performance by tuning intervals and enabling chunk skipping, see
the s documentation.
-
In Terminal, navigate to
<local folder>and connect to your .You use your connection details to fill in this connection string. -
Create tables for the data to import:
-
For the time-series data:
-
In your sql client, create a :
Create a for your time-series data using CREATE TABLE.
For efficient queries, remember to
segmentbythe column you will use most often to filter your data. For example:If you are self-hosting v2.19.3 and below, create a relational table, then convert it using create_hypertable. You then enable with a call to ALTER TABLE.
-
In your sql client, create a :
Create a for your time-series data using CREATE TABLE.
For efficient queries, remember to
-
For the relational data:
In your sql client, create a normal table:
-
For the time-series data:
-
Upload the dataset to your :
-
In Terminal, navigate to
-
Unzip crypto_sample.zip to a
-
Have a quick look at your data
You query s in exactly the same way as you would a relational table.
Use one of the following SQL editors to run a query and see the data you uploaded:
- psql: easily run queries on your s or self-hosted deployment from Terminal.
Enhance query performance for analytics
_CAP is the hybrid row-columnar storage engine, designed specifically for real-time analytics and powered by time-series data. The advantage of is its ability to seamlessly switch between row-oriented and column-oriented storage. This flexibility enables to deliver the best of both worlds, solving the key challenges in real-time analytics.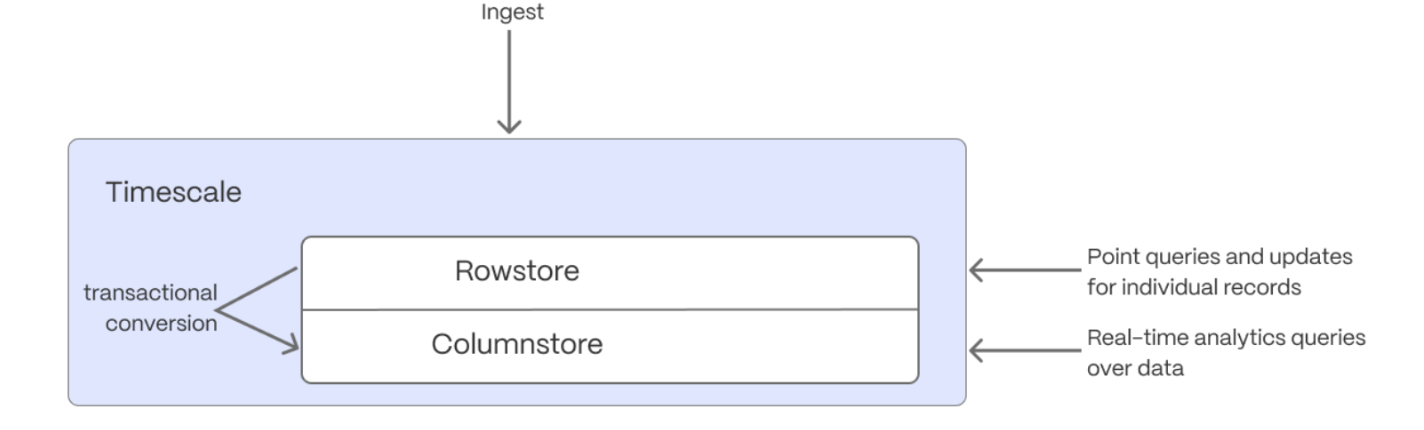 When converts s from the to the , multiple records are grouped into a single row.
The columns of this row hold an array-like structure that stores all the data. Because a single row takes up less disk
space, you can reduce your size by more than 90%, and can also speed up your queries. This helps you save on storage costs,
and keeps your queries operating at lightning speed.
is enabled by default when you call CREATE TABLE. Best practice is to compress
data that is no longer needed for highest performance queries, but is still accessed regularly in the .
For example, yesterday’s market data.
When converts s from the to the , multiple records are grouped into a single row.
The columns of this row hold an array-like structure that stores all the data. Because a single row takes up less disk
space, you can reduce your size by more than 90%, and can also speed up your queries. This helps you save on storage costs,
and keeps your queries operating at lightning speed.
is enabled by default when you call CREATE TABLE. Best practice is to compress
data that is no longer needed for highest performance queries, but is still accessed regularly in the .
For example, yesterday’s market data.
-
Add a policy to convert s to the at a specific time interval
For example, yesterday’s data:
If you have not configured a
segmentbycolumn, chooses one for you based on the data in your . For more information on how to tune your s for the best performance, see efficient queries. -
View your data space saving
When you convert data to the , as well as being optimized for analytics, it is compressed by more than
90%. This helps you save on storage costs and keeps your queries operating at lightning speed. To see the amount of space
saved, click
Explorer>public>crypto_ticks.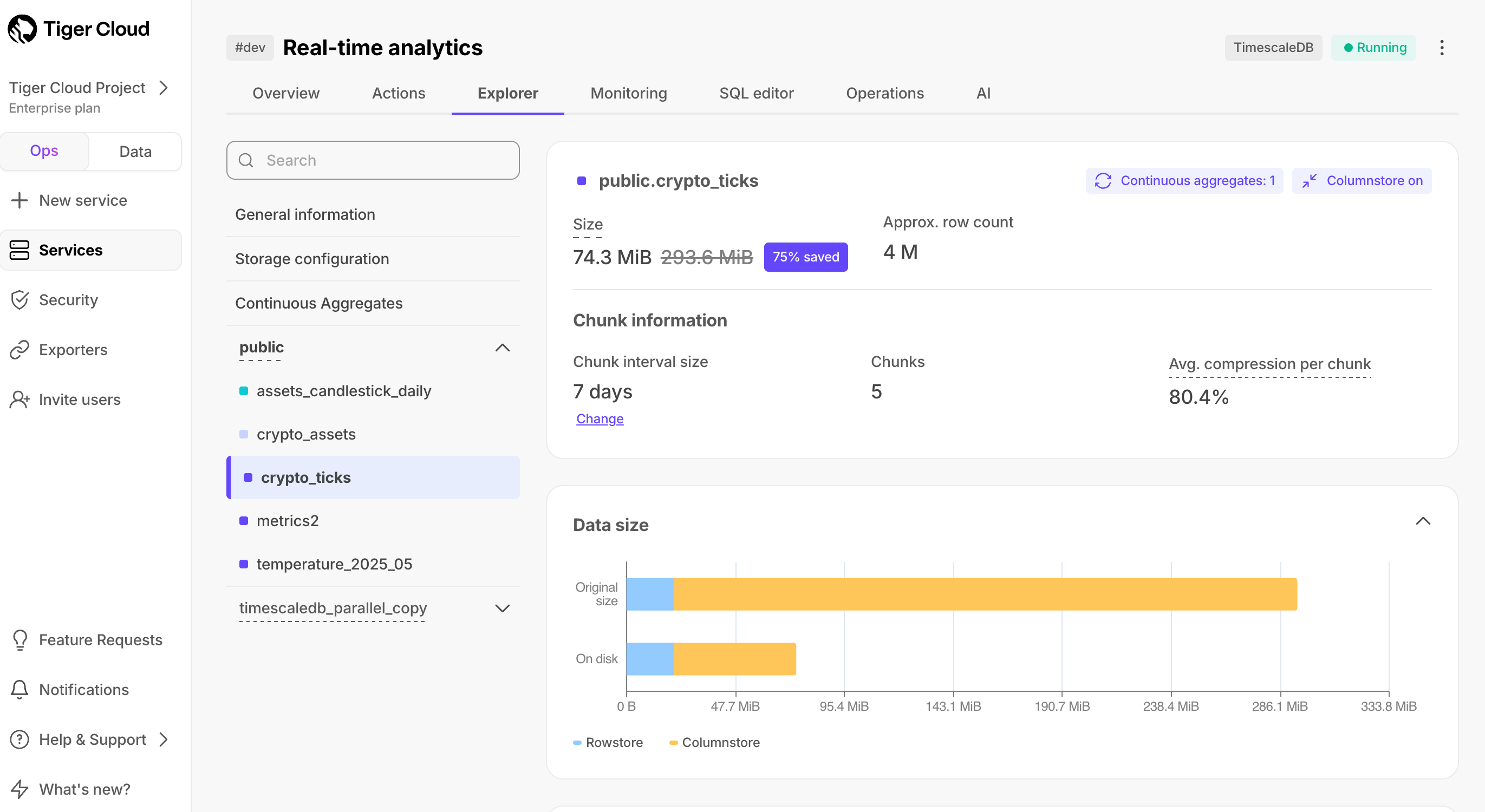
Write fast and efficient analytical queries
Aggregation is a way of combing data to get insights from it. Average, sum, and count are all examples of simple aggregates. However, with large amounts of data, aggregation slows things down, quickly. _CAPs are a kind of that is refreshed automatically in the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your dataset are tracked, and the behind the is automatically updated in the background.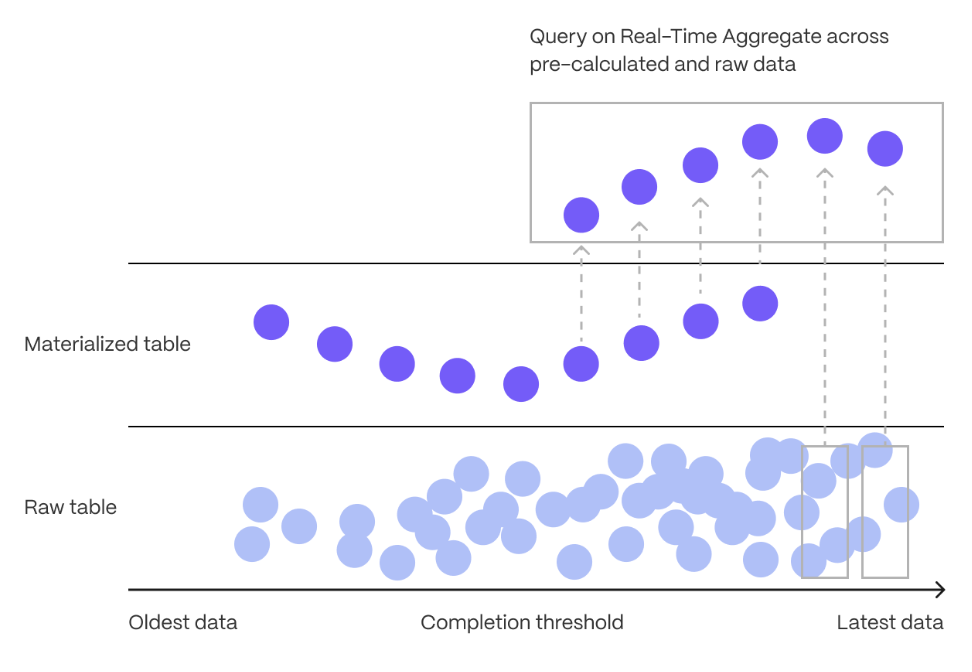 You create s on uncompressed data in high-performance storage. They continue to work
on data in the
and rarely accessed data in tiered storage. You can even
create s on top of your s.
You use s to create a . s aggregate data in s by time
interval. For example, a 5-minute, 1-hour, or 3-day bucket. The data grouped in a uses a single
timestamp. _CAPs minimize the number of records that you need to look up to perform your
query.
This section shows you how to run fast analytical queries using s and in
. You can also do this using psql.
You create s on uncompressed data in high-performance storage. They continue to work
on data in the
and rarely accessed data in tiered storage. You can even
create s on top of your s.
You use s to create a . s aggregate data in s by time
interval. For example, a 5-minute, 1-hour, or 3-day bucket. The data grouped in a uses a single
timestamp. _CAPs minimize the number of records that you need to look up to perform your
query.
This section shows you how to run fast analytical queries using s and in
. You can also do this using psql.
- Connect to your In , select your in the connection drop-down in the top right.
-
Create a
For a , data grouped using a is stored in a
MATERIALIZED VIEWin a .timescaledb.continuousensures that this data is always up to date. In data mode, use the following code to create a on the real-time data in thecrypto_tickstable:This creates the candlestick chart data you use to visualize the price change of an asset. -
Create a policy to refresh the view every hour
-
Have a quick look at your data
You query s exactly the same way as your other tables. To query the
assets_candlestick_dailyfor all assets:
SELECT ...GROUP BY day, symbol; ) and compare the results.
